Dental implants
- Home
- Dental implants
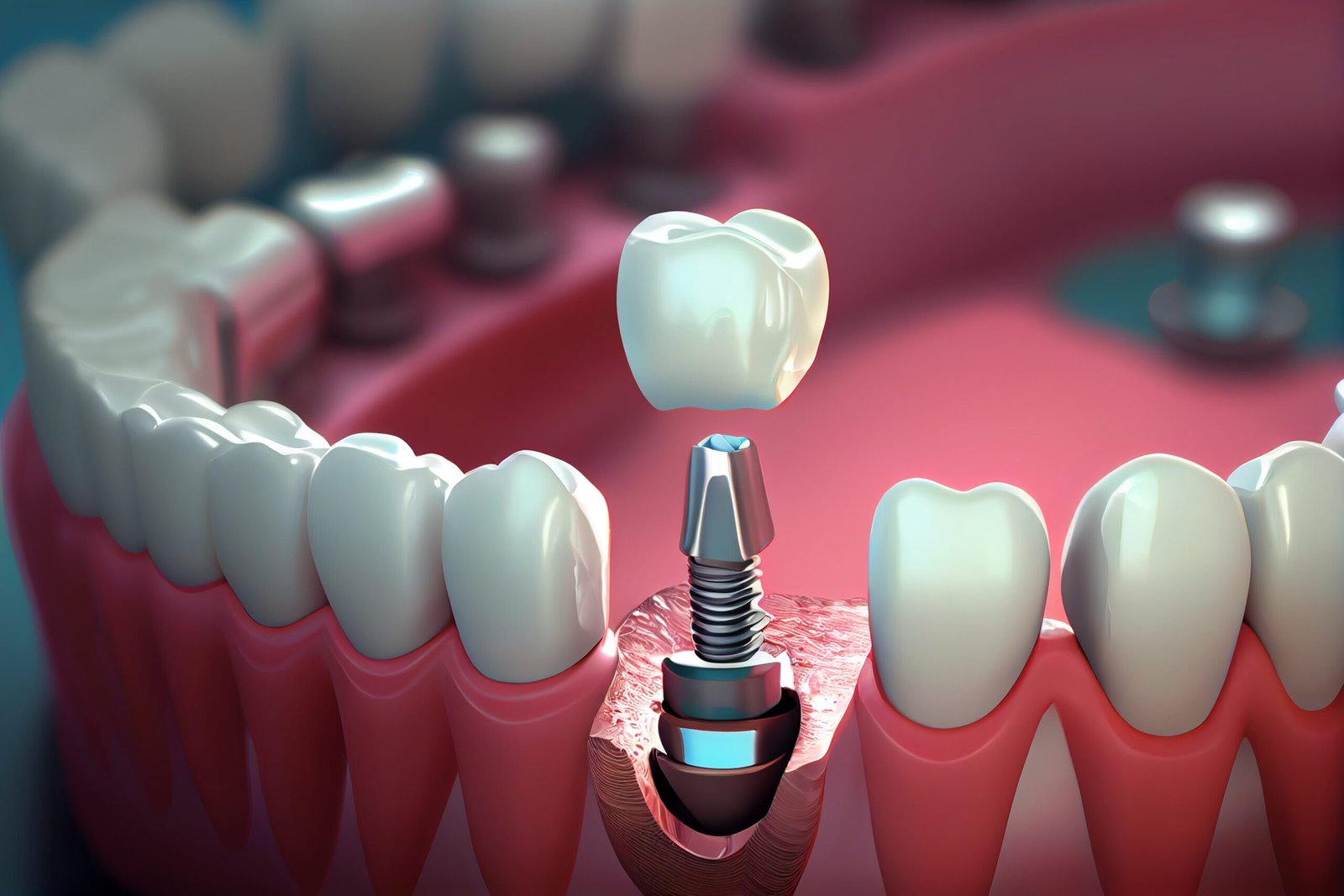

Dental implants
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots typically made of titanium or similar materials that are placed into the jawbone to support replacement teeth or bridges. They offer a long-term solution for individuals who have lost one or more teeth due to injury, periodontal disease, or other reasons.
Dental implants offer several advantages over other tooth replacement options, such as dentures or bridges. They look and feel like natural teeth, are durable, and can improve chewing and speech. Additionally, they help preserve jawbone integrity, as they stimulate bone growth and prevent bone loss, which can occur with missing teeth.
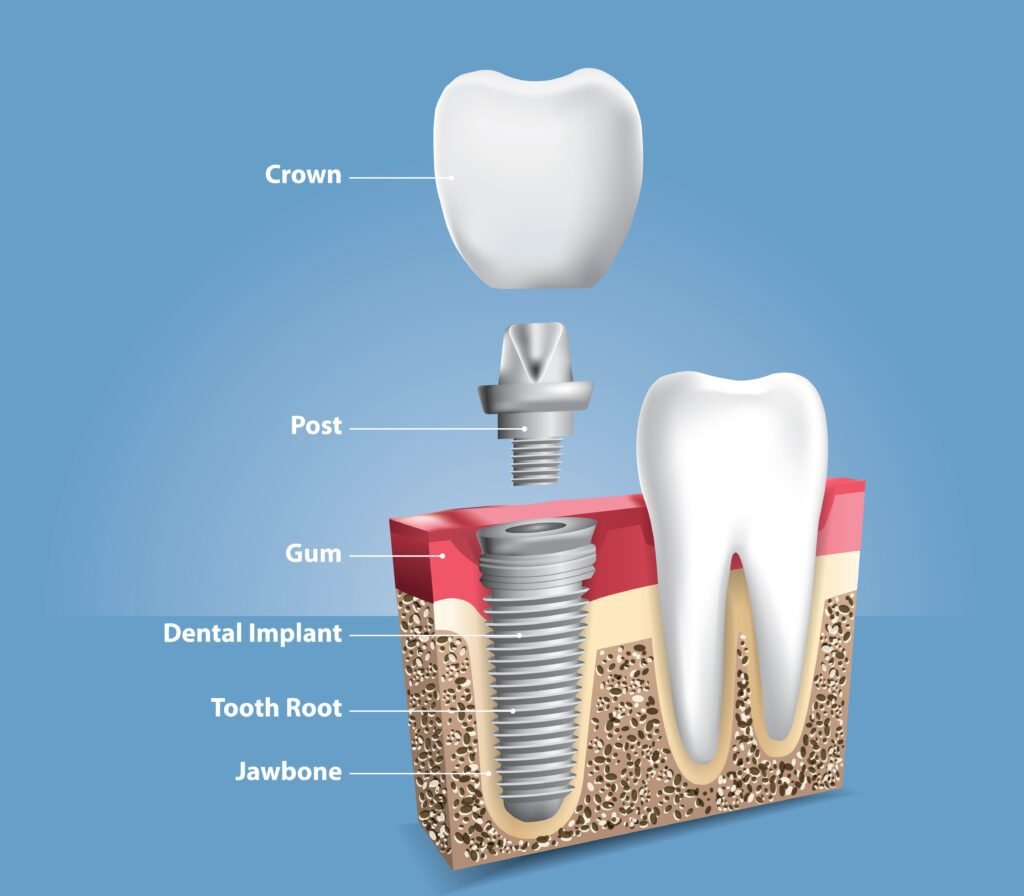

The process of getting dental implants usually involves several steps:
Initial Consultation: During this phase, your dentist or oral surgeon will examine your mouth, take x-rays, and discuss your medical history to determine if you’re a suitable candidate for dental implants.
Implant Placement: The dentist surgically places the implant into the jawbone beneath the gum tissue. The implant is then left to integrate with the bone, a process called osseointegration, which usually takes a few months.
Abutment Placement: Once the implant has fused with the jawbone, a small connector called an abutment is attached to the implant. This abutment will hold the replacement tooth or bridge in place.
Placement of Replacement Tooth: After the gums have healed around the abutment, the dentist will take impressions of your mouth to create a custom-made replacement tooth or teeth. These replacements are then attached to the abutment.
Dental implants offer several advantages over other tooth replacement options, such as dentures or bridges. They look and feel like natural teeth, are durable, and can improve chewing and speech. Additionally, they help preserve jawbone integrity, as they stimulate bone growth and prevent bone loss, which can occur with missing teeth.